Punjab Board Nots
Notes of Science for Class 8th
CHAPTER # 5
CHEMICAL REACTION
1) Define a chemical reaction.
The process in which a substance changes into entirely new substance with different chemical composition and properties is called chemical reaction.
2) What are reactants?
Substances which take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants.
A+B ---------> C+D In above reaction A & B are reactants.
3) What are products?
Substances which are formed in a chemical reaction are called products.
A+B ---------> C+D In above reaction C & D are products.
4) What is a chemical equation?
The representation of chemical reaction in terms of symbols, formulae and signs are called chemical equation. The reactants is written on left side while products on right sides.
A + B ---------> C + D
5) State law of conservation of mass
During a chemical reaction the total mass of the reactants is equal to the total mass of products.
6) Differentiate between.
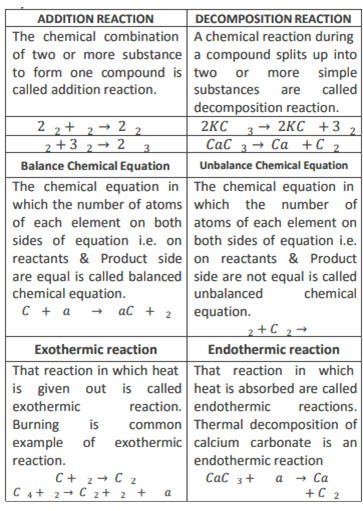
7) When coal burns it leaves ash behind. Ash so produced is lighter than the coal which has burnt. Justify the decrease in mass in the light of law of conservation of mass.
The decrease in mass of coal is due to the formation of gaseous products i.e. that escape into air and only lighter ash is left behind. So the total mass of reactants remains equal to the products.
8) Give two examples of following chemical reactions.
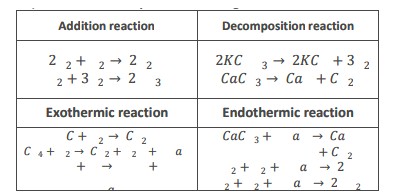
9) Describe application of chemical reactions.
i) Heat produced during burning of fuel is used to cook food.
ii) Energy produced during respiration is used to perform all the function of the body.
iii) Useful fermentation products e.g. yogurt and backing product are also application of chemical reaction.
iv) During photosynthesis in plants carbon dioxide and water react to produce glucose in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
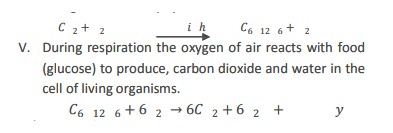
10) What is fermentation reaction?
Conversion of milk into yogurt and formation of baking products involve the chemical changes carried by microorganisms. Such reaction are called Fermentation
11) How chemical equation is written.
The reactants and products are separated by arrow. Reactants on left while products are written of right hand side of arrow. The arrow is directed toward products.
12) Write down the rules for balancing a chem.
Equation.
i) Firstly count the number of atoms of each element on both side of the arrow.
ii) Only balance one element at a time.
iii) Multiply the symbol or formula with suitable integers (2,3,4,5 etc) on that side of equation where the number of atom of a particular element is less and try to balance this element on both sides of equation
- Starts multiply with smaller number.
- Repeat the process for all the elements one by one.
- Balance the diatomic molecules like 2 , 2 , 2 at the end
Note: Solve all examples from Text Book
Describe the importance of exothermic reaction in everyday life.
- They are widely used to fulfill our needs of heat energy for various purposes.
- The heat released during burning of fuel at our homes is used for cooking food and to warm our rooms.
- Heat produced during digestion of food in our body
- keeps us warm and alive.
- Heat produced by Burning of fuel in thermal power station is used in generating electricity.
14) Give two examples of chemical reaction from everyday life which are essential for life.
Photosynthesis and respiration are the two essential chemical reactions for our life.
During photosynthesis in plants carbon dioxide and water react to produce glucose in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
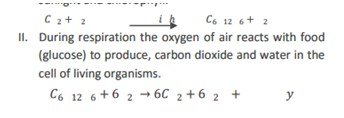
CHAPTER # 6
ACIDS, BASES / ALKALIES & SALTS
Define an acid.
Acids can be defined as the compounds which produce hydrogen ions (H+) in their aqueous solution. Acids have sour taste.
1. Name some mineral acids.
- Hydrochloric acid
- Nitric acid
- Sulphuric acid
- Phosphoric acid
2. State the properties of Acids
- All acids have sour taste
- All acids turn blue litmus solution and methyl orange solution Red.
- Strong acids are corrosive liquids. They burn skin and destroy fabrics and animal tissues.
- Aqueous solutions of acids are good conductors of electricity.
- Acids react with reactive metals (Mg, Zn) to form salt and evolve hydrogen.
3) Mention the uses of salts in industries
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) is used for the manufacture of chlorine, hydrogen chloride, caustic soda, washing soda and sodium hydrogen carbonate.
- Sodium carbonate is used for softening hard water and for the manufacture of glass and soap.
- Potassium nitrite is used for the preparation of gun powder, fireworks and fertilizer.
- Copper sulphate is used as fungicide in calico printing and in electroplating.
4. Name the salt which reduces acidity in our stomach.
Sodium chloride (NaCl)
5. What happens when a salt like copper sulphate reacts with water?
Sulphuric acid and copper oxide (CuO) is formed
4+2 → +2 4
6. Is soda water acidic or basic?
Soda water is acidic
7. Which alkali is commonly used to open a drain?
Potassium carbonate strong alkaline solution is used to open a drain.
8) Write down the reaction of ammonia and water.
3 + 2 4
Ammonia Water Ammonium Hydroxide
9) How litmus solution is prepared?
Litmus solution is prepared by dissolving red cabbage juice or turmeric powder.
11) What is the effect of dilute HCl on the colour of following?
|
Indicator |
Colour in dil HCl |
|
Methyl orange |
Red |
|
Phenolphthalein |
Colourless |
|
Blue litmus |
Red |
12) What is base? Write down the names and formulae of four bases.
Bases are the compounds that produce hydroxide ions
(OH-) in their aqueous solution.
Examples:
|
Sodium hydroxide |
NaOH |
|
Potassium hydroxide |
KOH |
|
Calcium hydroxide |
Ca(OH)2 |
|
Ammonium hydroxide |
NH4OH |
|
Magnesium hydroxide |
Mg(OH)2 |
13) State the properties of Bases
- Aqueous solution of a base has a soapy touch
- All bases turn Red litmus blue, colourless phenolphthalein pink and methyl orange yellow.
- Aqueous solutions of bases are good conductors of electricity.
- Bases react with acids to form salts and water. This reaction is called neutralization reaction.
+ → +
14) What is the action of caustic soda on the colour of following?
|
Indicator |
Colour after action of Caustic soda |
|
Red litmus |
Blue |
|
Phenolphthalein |
Pink |
|
Methyl orange |
Yellow |
15) Mention the sources of the following.
|
Name |
Source |
|
Citric acid |
Citrus fruits |
|
Tartaric acid |
Tamarind, Grapes |
|
Acetic acid |
Vinegar |
|
Formic Acid |
Ant’s string |
|
Oxalic acid |
Tomatoes |
|
Lactic acid |
Curd |
|
Malic Acid |
Apples |
|
Stearic acid |
Fats |
16) Describe how salts are useful for the human body
- Sodium and potassium salts are needed for the proper functioning of muscles and the nervous system.
- Salts of calcium are present in bones. They are responsible for the strength of bones. These salts are responsible for preventing heart attacks.
- Plaster of Paris (CaSO4 . ½ H2O) is used for broken limbs.
- Potash alum is used to coagulate the blood coming out of a wound. It is also used for the purification of water.
- Salts of iodine are needed for the proper functioning of thyroid glands. They are also used to set the treatment of goiter.
17) What happened when
i) Magnesium reacts with dilute HCl?
Magnesium forms its salt and release Hydrogen gas
ii) Copper oxide reacts with dil. Sulphuric acid
Copper salt and water are produced
+2 4→ 2+2
iii) Sodium reacts with chlorine
Sodium salt are produced which also used in cooking.
2 + 2→ 2
18) Why the aqueous solutions of NaHCO3 and Na2CO3 are basic in nature?
Because a strong base is formed
2 3+22→2+2 3
19) How does the soil become acidic?
Acid rain turns the soil acidic
20) Sulphuric acid molecule can give two protons in water whereas hydrochloric acid molecule can give only one proton. Does that mean sulphuric acid is twice as strong an acid as HCl?
Yes, 2 4 is twice as strong an acid as
21) Indicate in front of each salt the acid and the base which have been used to produce them.
22) Write the use of HCl
- For cleaning rust from the surface of metals.
- For purification of Common salt (NaCl).
- To make aqua regia (3HCl + HNO3) used to dissolve noble metals such as gold.
- For making glucose from starch.
- For the proper digestion of food in our stomach.
23) Write the use of Nitric Acid HNO3
- In the manufacture of fertilizers like ammonium nitrate
- For the manufacture of explosives
- In the manufacture of dyes, plastics and artificial silk.
- For etching designs on metals like copper brass and bronze.
|
Potassium |
Sulphuric Acid |
Hydroxide |
|
Magnesium nitrite |
Nitric Acid 3 |
Magnesium Hydroxide ( )2 |
|
Ammonium oxalate |
Oxalic Acid 𝐶2 4 |
Ammonium Hydroxide |
|
Sodium potassium tartarate 𝐾 𝑎𝐶4 4 6 |
Potassium Bitarate 𝐾 𝐶 4 4 6 |
Sodium carbonate 𝑎 2𝐶 3 |
|
Ferric chloride |
Hydrochloride Acid C |
Ferric Hydroxide ( )3 |
24) Write the use of Sulphuric acid
Sulphuric acid 2 4 used in:
- As a dehydrating agent
- In the manufacture of fertilizers like ammonium phosphate, calcium ammonium phosphate, calcium super phosphate etc.
- In the manufacture of celluloid plastic, artificial silk, paints, drugs and detergents.
- In petroleum refining, textile, paper and leather industries.
- In lead storage batteries.
25) Write the use of Acetic acid
Acetic acid used in:
- In the preparation of pickles (ACHAAR)
- In the manufacture of synthetic fiber.
26) Write the use of Sodium Hydroxide
Sodium hydroxide used in:
- Soap, textile and plastic industries.
- Petroleum refining.
- Making rayon
- In the manufacture of paper pulp and medicines.
27) Write the use of calcium Hydroxide ( )
Calcium hydroxide used in:
In the manufacture of bleaching powder II. As a dressing material for acid burns
In making lime sulphur sprays to be used as fungicide IV. As a water softener
For neutralization acidity present in soil
28) Write the use of ammonium Hydroxide
Ammonium hydroxide used in:
To remove grease from window panes
To remove ink spots from clothes III. As a regent in laboratory
For the treatment of bee’s string
29) What is PH Scale?
A scale used to measures the acidic or basic or alkaline solution is known as PH scale.
30) How we can measure PH of a solution?
The PH can be measure with universal indicator or PH paper. A universal indicator paper has a mixture of several dyes coated on it. It shows different colours for each PH values.
31) Define indicator
A substance shows different colour in acidic and basic solutions. e.g. phenolphthalein, methyl orange, litmus, turmeric, China rose and red cabbage.
32) What is Natural solution?
PH values range from 0 – 14. The solutions having equal concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) and hydroxide (OH-)
are neutral solutions. They have Ph = 7. PH = 7 is the midpoint of the scale.
Write the colours of some indicators in acidic and basic solutions
|
Indicator |
Original colour |
Colour in acid |
Colour in base |
|
Litmus |
Violet |
Red |
Blue |
|
Phenolphthalein |
Colourless |
Colourless |
Pink |
|
Methyl orange |
Orange |
Red |
Yellow |

Define Hydraulics
The branch of science deals with the transmission of fluid pressure through pipes as a source of mechanical force is called hydraulics. Such systems are often using to produce large force with the help of small force.
5) Define Pneumatics
The branch of science deals with the study of applications of pressurized gas to produce mechanical motion is called pneumatics.
6) State Pascal’s law
Liquid filled in a closed containers fluid exerts equal pressure in all direction. This fact was first discovered by Pascal and called Pascal’s Law.
7) What is an altimeter? Write its application
An altimeter is an instrument used to measure the altitude of an object above a fixed level. It is used in
- Air crafts
- Sky divers use wrist-mounted altimeter
Differentiate between hydrostatic and atmospheric pressure
|
Hydrostatic pressure |
Atmospheric pressure |
|
Greater the depth of the water in the vessel, greater is the pressure of water. Such a liquid pressure that increases with depth is called hydrostatic pressure |
The earth is surrounded by a cover of air called atmosphere. The pressure of atmosphere is called atmospheric pressure. 𝐴 ℎ 𝑖𝑐 = 𝑤 𝑖ℎ 𝑎𝑖 𝐴 𝑎 Pressure decreases with |
9) Why supporting wall of a dam is built very broad at the bottom?
The supporting wall of a dam is built very broad at the bottom because at bottom the water pressure is very large as compared to the surface of water.
10) Describe water pressure
The pressure exerted by water on the walls of the container and bottom is called water pressure.
Explanation:
It is observed that speed of water coming out of tap on ground floor is greater than the speed of water coming out of a tap on upper storey of our house. The speed of water depends upon the height of water. If water is on height then its speed is high and if water is at low height then its speed is also low.
11) Application of Pascal’s Law- hydraulic system Jack System
A small force F1 is applied on a small piston that produces pressure P on the oil. This Pressure P is transmitted through a pipe to a very large cylinder fitted with a piston. Since area of this piston is very huge. Hence a very large force is produced that is used to lift something very heavy like a car.
In figure valves V1 & V2 prevent the back flow of oil to the small cylinder so that heavy load remains rose up. When
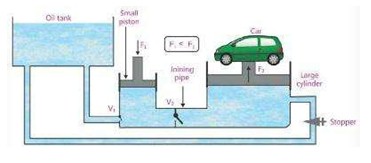
the oil stopper is opened, the oil in the large cylinder flows back to the oil tank and the load is brought down.
Brake System
It is a common example of a hydraulic system in a car. It consists of a pipe and two cylinders. The pipe is filled with
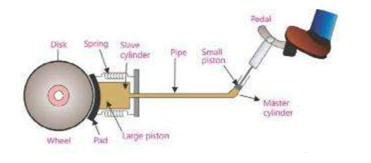
special fluid called brake oil. At one end of the pipe there is a cylinder fitted with a small piston called master cylinder. The small piston is connected with brake pedal. At the outer end of the pipe there is a second cylinder fitted with a large piston called slave cylinder. When small piston is pushed into master cylinder by applying a small force on brake pedal, the pressure thus produced is transmitted without loss to the slave cylinder. The large piston in the slave cylinder is pushed out with a large force. It pushes the brake pad out to make it rub against the moving wheel disc. It produces large frictional force which stops the running wheel.
12) Describe the use of Pneumatic system in daily life.
- Automatic tyres are inflated with compressed air.
- Spray guns use compressed air for spraying paints.
- III. Compressed air is used in air powered tools like hammers and drills
- It is also used in air brake system in heavy vehicles.
13) Describe Gas pressure in a container.
The molecules of a gas in container are in a continuous state of motion in all direction. There the molecule collides with each other and with the walls of the container. These collisions exert force on the walls of container and thus produce pressure.
14) What is aerosol?
“Sol” is a mixture of suspended solid or liquid particles in a gas or air. The product using “sol” systems are called aerosols.
Give six application of compressed air.
- Automobile tyres are inflated with compressed air for smooth running of vehicles.
- Spray guns use compressed air for spraying paint.
- III.Air powered motors use compressed air to work.
- Pneumatics
- Brake systems
- Most of dentistry tools use compressed air for their working.
CHAPTER # 8
MEASUREMENT OF PHYSICAL QUANTITIES
1) Describe physical quantity and examples
The quantities which can be measured are called physical quantity. Examples: Time, Mass, Length, volume etc.
2) Define the term prefix.
The words or letters added before SI units such as milli (m), centi (c) & Kilo (K) are known as prefixes.
Prefixes are based on multiplying and dividing the units by power of 10.
3) What is meter rule
It is a one meter long graduated stick. It is used to measure the length of an object or distance between two points. A meter rule is divided into 100 equal parts, each part is equal to one centi meter.
4) Write a short note on
Measuring Flask
Flask is laboratory vessels (container). The flask is made of plastic or glass. They are of different sizes and shapes. In school laboratory, 50ml, 100ml, 250ml, 500ml & 1000ml flask are used for making solutions.
Measuring Pipette
Pipette is used to transfer a measured volume of liquid from one container to another. They are of different sizes and shapes. In laboratory 10ml to 25 ml pipette of glass or plastic are used.
5) What are SI units? Explain.
International system of units: in our daily life, we often need to measure various physical quantities with the help of some standard quantity. For example if we purchase sugar, we must come to know the quantity of sugar. Thus, there is a need of some standard quantity for measuring unknown quantity. This standard quantity is called unit.
Table of Units
|
Physical quantity |
Symbol |
Unit |
Symbol |
|
Length |
l |
Metre |
m |
|
Mass |
m |
Kilogram |
Kg |
|
Time |
t |
Second |
s |
|
Volume |
V |
Cubic meter |
m3 |
- Write the names of measuring instruments which is used to measure the physical quantities.
|
Physical Quantity |
Measuring instrument |
|
Temperature |
Thermometer |
|
Mass |
Electrical balance |
|
Length |
Measuring tape |
|
Volume |
Measuring cylinder |
|
Time |
Watch |
|
Atmospheric pressure |
barometer |
Note: Solve all Numerical given at the end of chapter
CHAPTER # 9
SOURCES AND EFFECTS OF HEAT ENERGY
- Write down the effects of heating and cooling on
solids
Solid expand on heating and contract on cooling
- Write down the effects of heating and cooling on
gases
Gas expand on heating and contract on cooling
3) Why is water not used instead of mercury in thermometers?
Because Mercury has high coefficient of expansion per unit rise in temperature
4) Why one end of the iron girders is placed on rollers in construction of bridges?
One end of iron girders is placed on the rollers along with a gap at this end so that girder can move forward and backward during expansion or contraction.
- Why gaps are left between two sections of a railway track?
The gaps allow the expansion and contraction of rails during summer and winter season.
6) Why do hot air balloons rise up?
Since hot gases rose up in air, so hot air in balloon causes it to rise up.
- Why do gases expand faster than liquids and solids? Because the particles of gases are widely disturbed i.e. their particles are far apart from each other and they free to move. Other
- When a vessel containing a liquid is heated, the level of liquid initially falls and then rises up. Why does it
happen so? OR
Describe the irregular expansion of liquid.
On heating the liquid water from 0 0C to 4 0C, it contracts so the level of liquid initially falls. But after 4 0C it expands so liquid rises up.
- What is thermal expansion? Explain it with the help of experiment.
The expansion of material objects on heating is called thermal expansion.
- Take a metallic sphere which can pass easily through a ring.
- Remove the sphere out of the ring.
- III. Now heat the sphere and put it on the ring.
- It does not pass through the ring because of expansion due to heating.
- On cooling the sphere, it attracts and passes through the ring again.
10) What is Rivet and Riveting?
A rivet is a small, cylindrical and smooth shaft whose one end is swollen (called Head) while the other end is flat. Hot rivets are used to join the metal plates.
The process in which two metal plates are joined together by means of rivets is called riveting.
- Demonstrate how a bimetallic strip works in a thermostat.
In electric iron, when current passes through heating element, it becomes hot. The connected bimetallic strip also heats up. On getting hot, it bends and is disconnected from heating element so, circuit breaks and switches off the electric iron.
- Explain the peculiar (strange) behavior of water during contraction and expansion.
On heating the liquid water from 0 0C to 4 0C, it contracts and its volume decreases while its density increases. On cooling from 4 0C to 0 0C it expands, its volume increases and density decreases.
13) What is thermometer? How it works?
A thermometer is a device used to measure the temperature. When some hot object touch the bulb of the thermometer, the liquid inside the narrow tube expands and rises up and we can measure the temperature by reading scale.
- Explain the damages which are caused by expansion or contraction by giving two examples.
- In hot summer, the concrete used in roads expands. If no space is provided for its expansion, then road
- surface crack.
- Two sections of railway track are laid with gaps. If there are no gaps, then they may be de-shaped due to expansion in summer.
- Describe the effects of expansion and contraction of solids.
- In hot summer, concrete in roads expands and road surface crack.
- Two sections of railway track are laid with gaps. If there are no gaps, then they may be de-shaped due to expansion in summer.
- In bridges, one end of the iron girder resets on the rollers. A gap is also present at this end. So that it can move forward and backward during expansion and contraction.
- Explain the expansion of liquids and with the help of an experiment.
- Take an empty flask and fit a cork into its mouth. Pass short limb of U-shape glass tube through it.
- Clamp the flask in a stand.
- III. Dip the long limb of U-shaped tube in the water.
- Note and mark at the level of water in glass tube and then heat the flask.
- On heating, air in the flask expands and produces bubbles in the water.
- On cooling, air in the flask contracts, so suction is created which pulls the water in the glass tube up.
- Describe a simple experiment to study the thermal expansion of Gases.
- Take an empty flask and fit a cork into the mouth of the flask.
- Limb of the U shaped glass tube through the cork.
- III. Clamp the flask in a stand as shown in fig.
- Dip the long limb of U-shaped glass tube in the water.
- Note and mark a line at the level of water in the glass tube.
- Now heat the flask.
- VII. Stop heating and let the system cool down to room temperature.
- VIII. Observe and note the level of water in the glass tube again.
- The result is that the flask expands on heating and produce bubbles in water.
- On cooling flask contracts and water level is pulled up in the glass tube.
CHAPTER # 10
LENSES
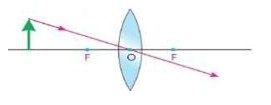
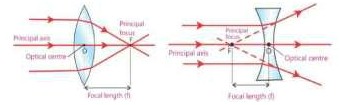
- Describe the paths of three rays which form image after passing through a convex lens.
i. A ray parallel to principal axis after refraction from a convex lens passes through its principal focus (F).
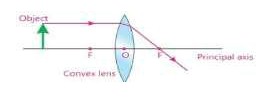
ii. A ray incident on the convex lens after passing through its principal focus (F) becomes parallel to principal axis.
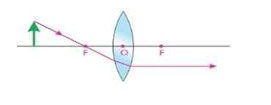
iii. A ray passing through the optical centre of the lens goes straight without changing its direction.
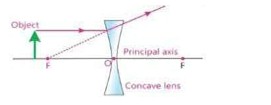
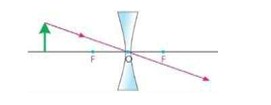
- Describe the paths of three rays which form image after passing through a concave lens.
i) A ray parallel to principal axis after refraction from a concave lens appears to come from principal focus (F).
ii) A ray pointing towards principal focus (F) becomes parallel to principal axis.
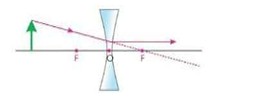
iii) A ray passing through the optical centre of the lens goes straight without changing its direction.
- Write the name of instrument in which convex lens is used
- Camera
- Binoculars
- Magnifying glass
- Contact Lens
- Define focal length.
The distance between the optical centre (O) and focus point (F) of the lens is called focal length (f). Focal length of a convex lens is taken as positive.
5) How focal length is affected when the lens of eye becomes thicker?
In order to look something near to eye, ciliary muscles make the lens thicker and its focal length becomes shorter. So the image is formed on retina instead of point beyond it.
6) Upon what factor does the amount of light entering in a camera depend?
The size of aperture.
- Can an image be obtained on the screen by a concave lens? Explain your answer briefly.
The ray diagram of concave lens for different positions of the object show that rays diverge out and do not meet on the other side of the lens after
refraction. Therefore real image is not formed, but virtual image is formed on extending the rays backward.
- How long our eye takes to acquire dark adoption at its maximum?
When we suddenly move from bright light to dark area, the cone cells become de-activated but rod cell do not activated immediately so we can’t see things clearly. But after some time rod cells becomes active and we are able to see in the darkness
i) Cone Cell: It activate in bright light II. Rod Cell: It activate in dim light
- Define short-sightedness and long-sightedness.
In short-sightedness a person can see near objects clearly but distant object appear blurred.
In long-sightedness a person can see distant objects clearly but near object appear blurred.
10) What is lens? Explain the difference between convex and concave lenses.
Lens: A lens is a piece of glass or other transparent material like plastic whose one or both side is spherical.
Types
There are two types of lenses.
- Convex lens
- Concave lens
Convex lens
Convex lens is thicker in the middle and thinner at the edges.
Concave lens
Concave lens is thinner in the middle and thicker at the edges.
11) Define centre of curvature
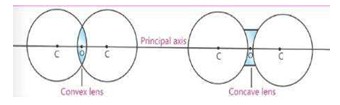
The centre of the sphere of which a lens is a part is called centre of curvature. It is denoted by “C”.
 12) Define Optical centre
The centre of the lens is called optical centre. It is denoted by "O"
12) Define Optical centre
The centre of the lens is called optical centre. It is denoted by "O"
13) Define principal axis and optical axis.
The line passing through the optical centre and centre of curvature of the faces of the lens is called principal axis or optical axis.
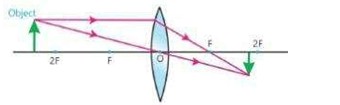
Explain the ray diagram where the images would be formed by convex lens for different distances of object. Also discuss the nature of images.
i) When object is placed beyond 2F, then image is formed between F and 2F. The image is real, inverted and smaller in size.
ii) When object is placed at 2F, then image is formed at 2F. The image is real, inverted and equal in size.
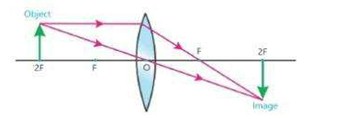
iii) When object is placed between F and 2F, then image is formed beyond 2F. The image is real, inverted and larger in size.
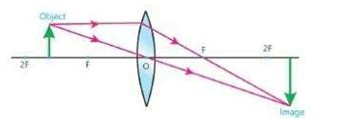
iii) When object is at F then image is formed at infinity (∞)
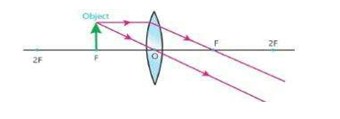
15) What is a real and virtual image?
Real image
The image that can be obtained on the screen is called real image.
Virtual image
The image that cannot be obtained on the screen is called virtual image.
- Why is real image not formed by concave lens? Explain your answer by ray diagram.
In case of concave lens the ray diagram for different positions of the object show that rays diverge out and do not meet on the other side of the lens after refraction. Therefore real image is not formed. Virtual image is formed on extending the rays backward. The image is always virtual erect and smaller in size.

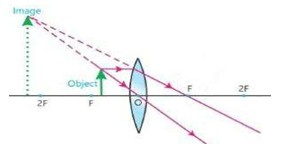
17) Explain how eyes get used to darkness after sometime
When we suddenly move from bright light to dark area, the cone cells become de-activated but rod cell do not activated immediately so we can’t see things clearly. But after some time rod cells becomes active and we are able to see in the darkness
- Cone Cell: It activate in bright light
- Rod Cell: It activate in dim light
Explain the defects in human eye.
- Short-sightedness (Myopia)
In short-sightedness a person can see near objects clearly but distant object appear blurred.
Reason
When the eye lens becomes much thicker or eyeball becomes too long, the image of distant object is formed in front of the retina rather at retina. This defect is also called Myopia.
Correction of the Defect
This defect is removed by using concave lens of suitable
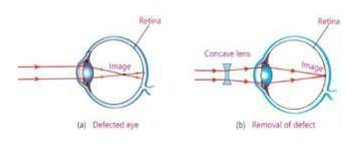
focal length (f). The concave lens diverges the light rays before they enter the eye. Hence the rays again meet at the retina.
- Long-sightedness (Hyperopia)
In long-sightedness a person can see distant objects clearly but near object appear blurred.
Reason
When the eye lens becomes thin or eyeball becomes too short, the image of near object is formed beyond the retina rather at retina. This defect is also called Hyperopia.
Correction of the Defect
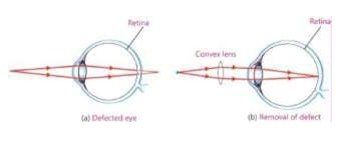
This defect is removed by using convex lens of suitable focal length (f). The convex lens converge the light rays before they enter the eye. They are further bent by the eye lens to meet at the retina.
- How do camera and human eye resemble with each other? What is the difference in their actions?
Similarities
- The retina of eye and film of camera serve the same purpose.
- Like camera, the eye lens forms a real and inverted image.
- Pupil of eye is similar to the aperture of camera.
Differences
In a camera lens can be moved back and forth the image on film but eye lens cannot move.
20) Identify the properties of convex and concave lens
Properties
|
Properties |
Convex lens |
Concave lens |
|
Positive focal length |
||
|
Negative focal length |
||
|
Thicker in the middle |
||
|
Thinner in the middle |
||
|
Can form real image |
||
|
Diverging lens |
||
|
Always forms virtual image |
||
|
Converging lens |
CHAPTER # 11
ELECTRICITY IN ACTION
1) State the Principle of Power Generator
The basic principle is that the coils are kept stationary while magnet is turned inside the coil. The stationary coil is called stator. The moving magnet is called rotor.
- What are input devices? Give at least three examples.
Any device that changes non electrical energy into electrical energy in an electronic system is called input devices.
Examples: Key board, mouse and microphone.
- What are output devices? Give at least three examples.
An output device converts electrical energy into other forms of energy
Examples: Loud speaker, T.V screen, Monitor, Printer.
4) What is the difference between A.C and D.C?
|
A.C (Alternating current) |
D.C (Direct current) |
|
The current which changes its direction after an equal interval of time is called Alternating current (A.C) |
The current which do not changes its direction after an equal interval of time is called Direct current (D.C) |
|
Examples |
|
|
Generators |
Cell, Batteries |
- Name some basic components of electronics system Resistors
- II.Capacitors
- III.Transistors
- Silicon chips
- Integrated circuits (IC)
- Semiconductor diodes
- What is the function of solar panel?
- It converts solar energy into electrical energy.
- Solar energy is used through solar panels.
- During day light, electricity is directly used to run appliances and can also be stored in batteries for the use during night.
Sketch an electrical generator and its important parts
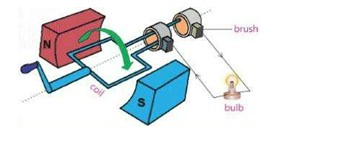
Describe the working of power generator
The basic principle is that the coils are kept stationary while magnet is turned inside the coil. The stationary coil is called stator. The moving magnet is called rotor.
The running water or fuels like, coal, oil or gas are used to run generators for producing electricity.
In coal-fired electricity generation, the burning coal heats water in a boiler to produce steam. The steam pushes the blades of a turbine fixed at the lower end of the rotor shaft. As the rotor spins inside the stator, electric power is generated.
- Discuss the problems involved in
- Hydro power generation
- Thermal power generation
- Solar power generation
Hydro power generation
This is traditional method of producing cheap electricity but involve some problems
- The people living in these areas where the dams to be constructed are shifted to some other places.
- In winter, its capacity decreases due to shortage of water.
- Water table near a dam rises due to which water logging occurs and the land becomes uncultivated.
Thermal power generation
- This method involves burning of fossil fuels (Oil, gas, Coal). These are non-renewable sources.
- Fossil fuels releases smoke and other harmful gases in atmosphere.
Solar power generation
- Very high installation cost
- Not applicable for night
- Number of batteries required
- What is bicycle dynamo?
The dynamo is a small generator which produces electricity from the energy of your body when you pushing pedal. Some bicycle may have a dynamo to light up its lamp.

- What is hydel power generation?
It is very economical, environmental friendly method. In this method water falls from a high lake on the blades of a turbine and it starts rotating. This rotating turbine runs the generators that produce electricity. The electricity is transmitted through wires to the whole country.
12) What is solar energy?
The energy produced by sun is called solar energy. This energy is produced by solar panels.
13) What is wind energy?
The energy produced by wind is called wind energy. The kinetic energy (K.E) of wind in coastal areas is use to turn huge blades mounted on high pole. This rotating blade runs the generators that produce electricity.
14) What is nuclear energy?
The energy produced by nucleus of an atom is called nuclear energy. It is produced by nuclear fission.
15) What is nuclear fission?
Breaking a heavy nucleus into smaller atoms by fast moving neutrons is called nuclear fission. A large amount of energy is released by this process.
16) Define semiconductor.
Semiconductors are materials in which motions of electrons can be controlled. The most common example is silicon.
17) Define semiconductor diodes.
It is a device in which electric current can flow in one direction. It has 2 terminals P and N.
18) What is transistor?
It is a semiconductor device with three terminals. It is used for switches.
19) What is integrated circuit (IC)?
Very tiny electronic circuits are called integrated circuits (IC).
CHAPTER # 12
EXPLORING SPACE
- How does reflecting telescope differ from refracting telescope?
Reflecting telescope can be made much larger than a refracting telescope, so that a better and bright image can be seen.
2) What are rockets?
Rocket is a space tool by which spacecrafts, space shuttles and space stations are transfer into space. The sites from which rockets are launched into space are called rocket launching pads.
- What is advantage of putting a telescope in space? Telescope is an instrument that helps to see lovely object. Hubble telescope can produce clear images of astronomical objects which are very far from the earth.
- What is remote sensing?
Fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, natural gas) and underground water reservoirs can be located with the help of satellites. This study is called remote sensing.
5) What is GPS?
GPS stands for Global positioning system.
- Describe the benefits generated by technology of space exploration.
Health and medicine
- The invention of WARP 10 and hand-held high intensity LED unit etc. these machines are used for getting relief in muscle and joint pains and arthritis
- Infra-red (IR) thermometer
- Kidney dialysis machines and mini cameras for taking photos of internal organs of human body.
- The materials used to keep our homes warm.
Global Navigation
- Geostationary orbits and GPS use the network of satellites to facilitate communication and navigation.
- The travelers, aeroplane pilots, sailors and desert hikers also use GPS in mobile phones to find their positions and maps.
Weather forecasting
- The accurate weather reports on hourly basis are possible by the help of satellites.
- It is very easy to predict natural calamities such as floods, storms and tornadoes.
Advanced electronics and computers
Satellites are fitted with electronic and computer systems that can perform many function automatically.
Locating Minerals, Fossil Fuels and water reservoirs
Fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, natural gas) and underground water reservoirs can be located with the help of satellites. This study is called remote sensing.
- Explain how do astronauts survive and work in space.
- Pressurized section in which scientists work without space suits.
- Open to space section on which equipment is mounted for observing the earth and sky. Unprotected human body cannot survive more as liquid boils at low
pressure.
- The astronauts wear a specially designed suit called space suit to protect from hazards while going into
space.
- Special foods are prepared and packaged for easier transportation and a variety of tastes for the astronauts.
- Describe the technological tools used in space exploration.
1. Space rockets
It is used for transporting spacecrafts, space shuttles and space stations into the space.
2. Rocket launching pads
The place where rockets are launched into space is called rocket launching pads. These are especially built platforms for firing rockets into space.
3. Telecommunication system
It is installed in rocket and spacecraft so that space crew in the rockets capsule can communicate with each other and with earth station.
4. Ground mission control stations
To monitor and guide their motion in space, Ground stations receive and process information from satellites. The main tasks are:
Tracking
Continuously reporting the position of the satellite or space probe.
Monitoring
- Progress of a space mission is closely observed and necessary instructions are issued from time to time.
- Describe four problems created from space exploration and their solutions.
The main problems are:
- Space sickness
- Effects of weightlessness
- Conditions resulting from exposure to radiation
- Many unwanted side effects
- Disposal of rocket parts
- Pollution caused by burning of rocket fuel
Deaths in space missions
Many deaths have resulted during the manned space flights. Space scientist needs continuous work to improve safety in space mission.
Fell of space crafts
In 1979 skylab fell from its orbit to earth. This type of incidents very dangerous for populations
Very costly space programs
Space programs are very costly. Involvement of private sector in mission could be a possible solution.
10) Write short notes on the following:
Hubble Space Telescope
It is the first space based reflecting telescope launched in 1990. It revolve around earth at a height of 600 Km. it is work 24 hours. It has taken clear pictures of galaxies, billions of Kilometers away in space.
Space Probe or Space crafts
It is a vehicle designed to travel in space. It is used for different purposes like communication, earth’s observation and transportation of humans. There are two major types
(I) Robotic space craft (II) Manned space
craft
Robotic space craft
It is sent into space for collection of data about space, planets and other heavenly bodies such as asteroids. Voyager I and voyager II are the two examples.
Manned Space craft or probe
It carries humans and equipment to space. It is larger and contains necessary facilities for humans such as
- Oxygen
- Pressurized cabins III. Food
- Water
- Specially built bathrooms.
It also protects humans from harmful radiations.
Space Stations
Either very long stay or performing experiments in space, larger space craft called space stations are used. A space station is built in space by carrying its many small parts and then assembling them there. It may have T.V, bags for sleeping and kitchen for fresh food.
Notes of Science Chapter 1 to 4
Notes of Science Chapter 5 to 11